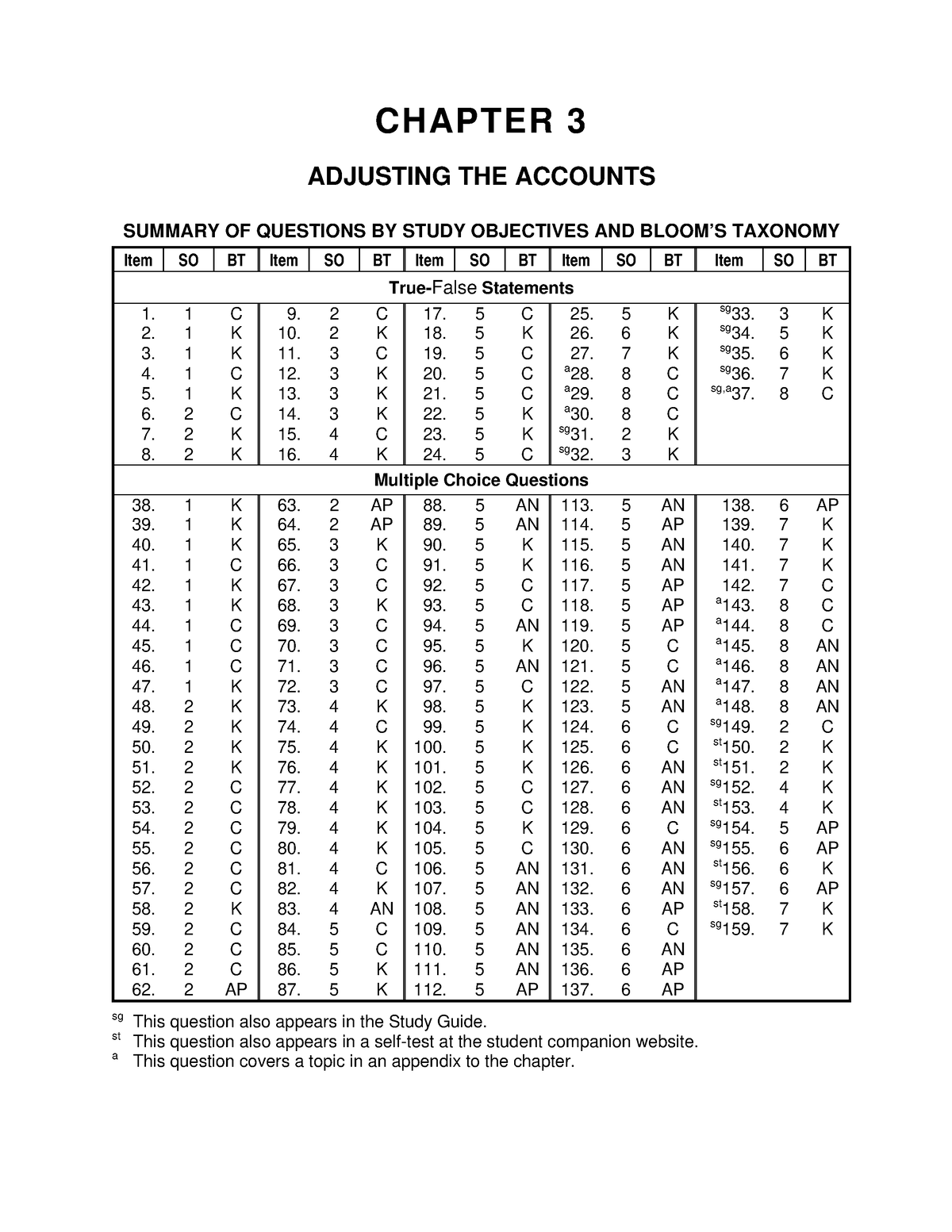
Interest Receivable increases (debit) for $1,250 because interest has not yet been paid. Interest Revenue increases (credit) for $1,250 because interest was earned in the three-month period but had been previously unrecorded. During the year, it collected retainer fees totaling $48,000 from clients. Retainer fees are money lawyers collect in advance of starting work on a case. When the company collects this money from its clients, it will debit cash and credit unearned fees. Even though not all of the $48,000 was probably collected on the same day, we record it as if it was for simplicity’s sake.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Depreciation may also require an adjustment at the end of the period. Recall that depreciation is the systematic method to record the allocation of cost over a given period of certain assets. This allocation of cost is recorded over the useful life of the asset, or the time period over which an asset cost is allocated. The allocated cost up to that point is recorded in Accumulated Depreciation, a contra asset account.
Types
The same is true about just about any asset you can name, except, perhaps, cash itself. Journal entries are recorded when an activity or event occurs that triggers the entry. Recall that an original source can be a formal document substantiating a transaction, such as an invoice, purchase order, cancelled check, or employee time sheet. Not every transaction produces an original source document that will alert the bookkeeper that it is time to make an entry.
Prepaid expenses
To begin, the bookkeeper or accountant must identify the need for an adjustment entry. This could be due to an error in the original journal entry, the need to accrue expenses or revenue, or the need to record depreciation. The revenue recognition principle requires businesses to recognize revenue when it is earned, regardless of when payment is received. Adjustment entries are necessary to ensure that revenue is recognized in the correct period, even if payment has not been received. The matching principle is a fundamental accounting principle that requires expenses to be matched with the revenues they generated. Adjustment entries ensure that all expenses and revenues are recorded in the correct period, even if they were not initially recorded.
Knowing when money changes hands, as opposed to when your business first recognised income or expenses, is important. That’s why it’s essential to understand basic accounting adjusting entries in greater depth. Entries are made with the matching principle to match revenue and expenses in the period in which they occur. Adjustments reflected in the journals are carried over to the account ledgers and accounting worksheet in the next accounting cycle. Also known as accrued liabilities, accrued expenses are expenses that your business has incurred but hasn’t yet been billed for.
- In such a case, the adjusting journal entries are used to reconcile these differences in the timing of payments as well as expenses.
- The other deferral in accounting is the deferred revenue, which is an adjusting entry that converts liabilities to revenue.
- And each time you pay depreciation, it shows up as an expense on your income statement.
- Understanding adjustment entries is critical for anyone involved in accounting, finance, or business operations.
ACCOUNTING for Everyone
The transactions which are recorded using adjusting entries are not spontaneous but are spread over a period of time. Not all journal entries recorded at indirect tax definition the end of an accounting period are adjusting entries. For example, an entry to record a purchase on the last day of a period is not an adjusting entry.
This can happen when estimates are not updated or when they are based on incorrect assumptions. To avoid this mistake, it is important to review and update estimates regularly. There are a few other guidelines that support the need for adjusting entries. One difference is the supplies account; the figure on paper does not match the value of the supplies inventory still available. This is extremely helpful in keeping track of your receivables and payables, as well as identifying the exact profit and loss of the business at the end of the fiscal year. Learn how to build, read, and use financial statements for your business so you can make more informed decisions.
Without adjustment entries, the financial statements would not be a reliable source of information for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders. In such a case, the adjusting journal entries are used to reconcile these differences in the timing of payments as well as expenses. Unearned revenues are payments for goods/services that are yet to be delivered. For example, if you place an order in January, but it doesn’t arrive (and you don’t make the payment) until January, the company that you ordered from would record the cost as unearned revenue.







